
As the gardening season shifts from summer to autumn, many horticulturists and home gardeners are turning to a specific chemical compound to extend the life and vibrancy of their floral displays. The use of potassium nitrate as a late-season fertilizer is a practice that has been gaining widespread attention for its ability to encourage robust flowering and improve plant resilience as temperatures begin to cool. The compound provides two essential macronutrients potassium (K) and nitrogen (N) which are critical for plant development, particularly during the flowering phase.
The Role of Potassium and Nitrogen in Plant Health
The shift in seasons presents a unique challenge for flowering plants. Shorter daylight hours and cooler temperatures can signal the end of a plant’s growing cycle, often leading to a reduction in flower production. Gardeners are increasingly relying on targeted fertilizers to counteract these natural processes. According to a report from the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), potassium and nitrogen are among the most crucial elements for plant health. Nitrogen primarily supports vegetative growth, including stems and leaves, while potassium is vital for overall plant function, regulating water movement and nutrient transport.
Dr. Anya Sharma, a senior horticultural scientist at the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI), explains the synergistic relationship. “While nitrogen is essential for building the plant’s foundational structure, potassium is the key player in reproductive processes,” she said in a recent interview. “Potassium strengthens cell walls, enhances disease resistance, and is fundamental for flower and fruit development. Providing a plant with a balanced dose of both nutrients, especially as environmental conditions change, can significantly prolong its blooming period.”
How Potassium Nitrate Works
Potassium nitrate, with the chemical formula KNO₃, is a highly soluble compound that can be applied to plants as a granular fertilizer or a liquid feed. Its high solubility means the nutrients are readily available for plant roots to absorb. The compound is prized for its high percentage of potassium, often containing around 13% nitrogen and 46% potassium oxide, though formulations can vary. This high potassium-to-nitrogen ratio is what makes it particularly effective for boosting flower production.
When a plant is in its vegetative stage, it requires more nitrogen to produce foliage. As it prepares for flowering, its nutritional needs shift. A higher demand for phosphorus and potassium emerges to support the development of buds and flowers. Potassium nitrate addresses this need by providing a concentrated dose of the latter two elements. The potassium component specifically aids in the activation of enzymes responsible for protein synthesis and carbohydrate metabolism, which are crucial for producing large, colorful blooms.
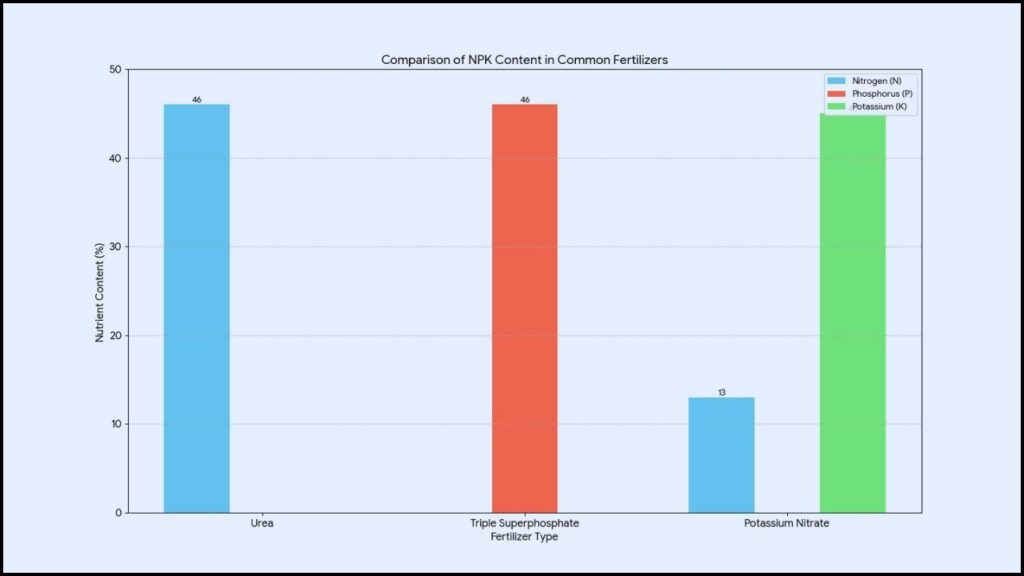
The Benefits of Using Potassium Nitrate for Fall Blooms
Using this specific fertilizer in the latter part of the growing season offers several distinct advantages beyond just prolonged flowering.
1. Enhanced Plant Vigor and Disease Resistance: The potassium in the compound strengthens the plant’s cellular structure, making it more resilient to stress from early frosts and temperature fluctuations. This increased hardiness helps the plant withstand potential damage from fungal diseases and pests that may become more prevalent in damper, cooler weather.
2. Improved Flower Quality: According to a study published in the Journal of Horticultural Science & Biotechnology, plants treated with adequate potassium exhibited not only a greater number of flowers but also more vibrant colors and stronger stems. This is because potassium directly influences the synthesis of pigments and the structural integrity of the plant.
3. Nutrient Efficiency: As a nitrogen-containing fertilizer, potassium nitrate offers an advantage over pure potash (potassium carbonate) because the nitrogen component aids in the plant’s ability to absorb and utilize the potassium more efficiently. “It’s not just about applying the nutrients; it’s about making sure the plant can actually use them,” said Dr. Liam Chen, a professor of soil science at the University of California, Davis. “The presence of nitrogen helps drive that metabolic process, making the fertilizer highly effective.”
Application and Considerations for Gardeners
While the benefits are clear, experts advise caution and careful application. Over-fertilization with any compound can lead to nutrient burn, a condition where excessive salts in the soil damage a plant’s roots. The recommended application method is often a foliar spray or a diluted liquid feed applied directly to the soil around the base of the plant. This allows for precise control of the dosage.
“The key is to apply it in moderation and at the right time,” says Emily Carter, a master gardener and author of The Year-Round Garden. “I typically recommend starting a light application in late summer and continuing every two to three weeks until the first hard frost. This provides a steady supply of nutrients without overwhelming the plant.”
The effectiveness of any fertilizer also depends on existing soil conditions. Soil tests are recommended to determine baseline nutrient levels before applying any amendments. For home gardeners without access to a lab, many agricultural extension offices provide affordable testing services.
The use of potassium nitrate represents a more scientific approach to gardening, moving beyond traditional methods to provide plants with precise nutritional support. As climate patterns become more variable, strategies for extending growing seasons are expected to gain further traction among both professional growers and hobbyists.
